Ureteroscopy
Make an Appointment
Our team is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need.
Ureteroscopy
Treatment Overview
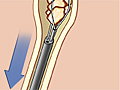
A ureteroscopy is a type of procedure. Your doctor may do it to remove kidney stones from one of your ureters. These are the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder. Your doctor may also do it to help find the reason for a urinary infection or blood in your urine.
Your doctor puts a thin scope with very small tools in it into your urethra. This is the tube that carries urine from your bladder to the outside of your body. Then the doctor moves the scope through your urethra and bladder into your ureter.
The doctor may use a wire with a tiny basket on the end to take out a kidney stone. Or the doctor may use a laser to break up a stone. If this is done, the pieces will wash out of your body in your urine.
You may be awake during the procedure. Or you may have medicine to make you sleep. In either case, you will not feel pain.
What To Expect
Most people are able to go home the same day of the procedure. But you may need to stay in the hospital. If you do, the stay is usually no more than 24 to 48 hours.
For several hours after the procedure you may have a burning feeling when you urinate. This feeling should go away within a day. Drinking a lot of water can help. Your doctor also may advise you to take medicine that numbs the burning. This medicine is called phenazopyridine. It is available by prescription and over the counter. Brand names include Pyridium and Uristat.
You may have some blood in your urine for 2 or 3 days.
Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic for a day or two. This will help prevent an infection.
Why It Is Done
Urologists use ureteroscopy to remove stones that are stuck in the ureter and are closer to the bladder than the kidney (in the lower third of the ureter). But newer technology is allowing ureteroscopy to be used even for small stones in or near the kidney.
Risks
Complications are more likely when the stone is close to the kidney (upper third of the ureter) and include:
- Injury to the ureter.
- Urinary tract infection.
- Bleeding.
- Abdominal (belly) pain.
Credits
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.